Technical Information
The difference in shell color of farmed vannamei shrimp and its causes
Color is an important factor that determines the choice of food by consumers, and it also determines the value of farmed shrimp. The article compares the color of shrimp shells and the causes leading to the difference of whiteleg shrimp shells.
The color of shrimp is largely influenced by pigment, feed, animal, disease status and environmental factors. The report of scientists analyzed the difference between two common colors of white shrimp, which are white shell shrimp and red brown shrimp.
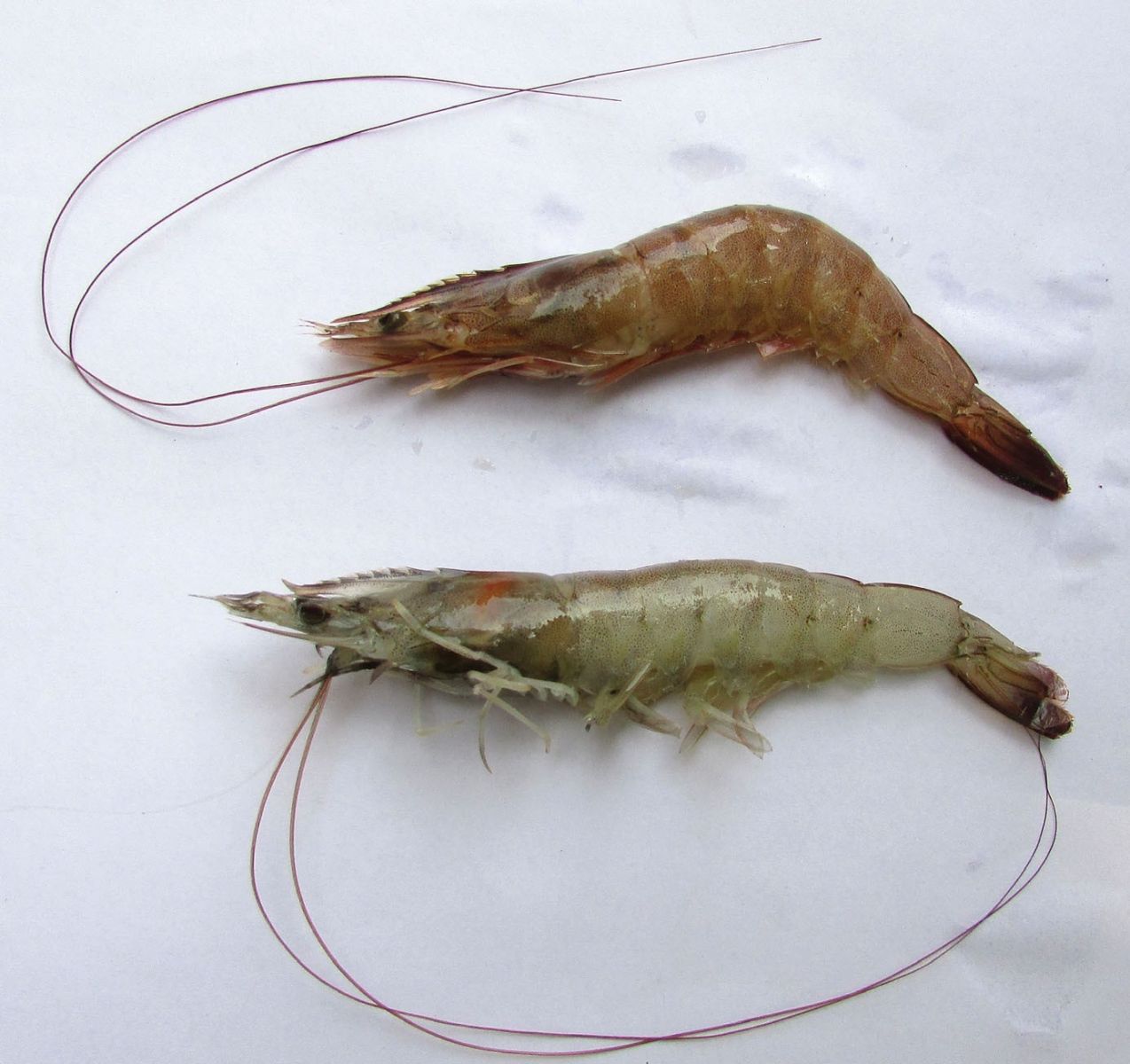

The normal shell color of farmed vannamei is bluish-white (bottom), but there are a few with brown shells (top).
Compare 2 types of white shrimp shell color
In terms of physical aspect, except for the color difference, white-green shrimp and brown-shelled white shrimp have similar characteristics.
A study was conducted to determine if there was a difference between white-shelled shrimp and brown-shelled shrimp in terms of flesh color, meat composition, and meat texture.
Shrimp collected from a shrimp farm in Andhra Pradesh, India were randomly selected and transported at <4 °C to the laboratory and analyzed.
Conduct experiments
Color analysis
1: Peel fresh shrimp to analyze the color of each type of 5, 2: Cook for 5 minutes of each type.
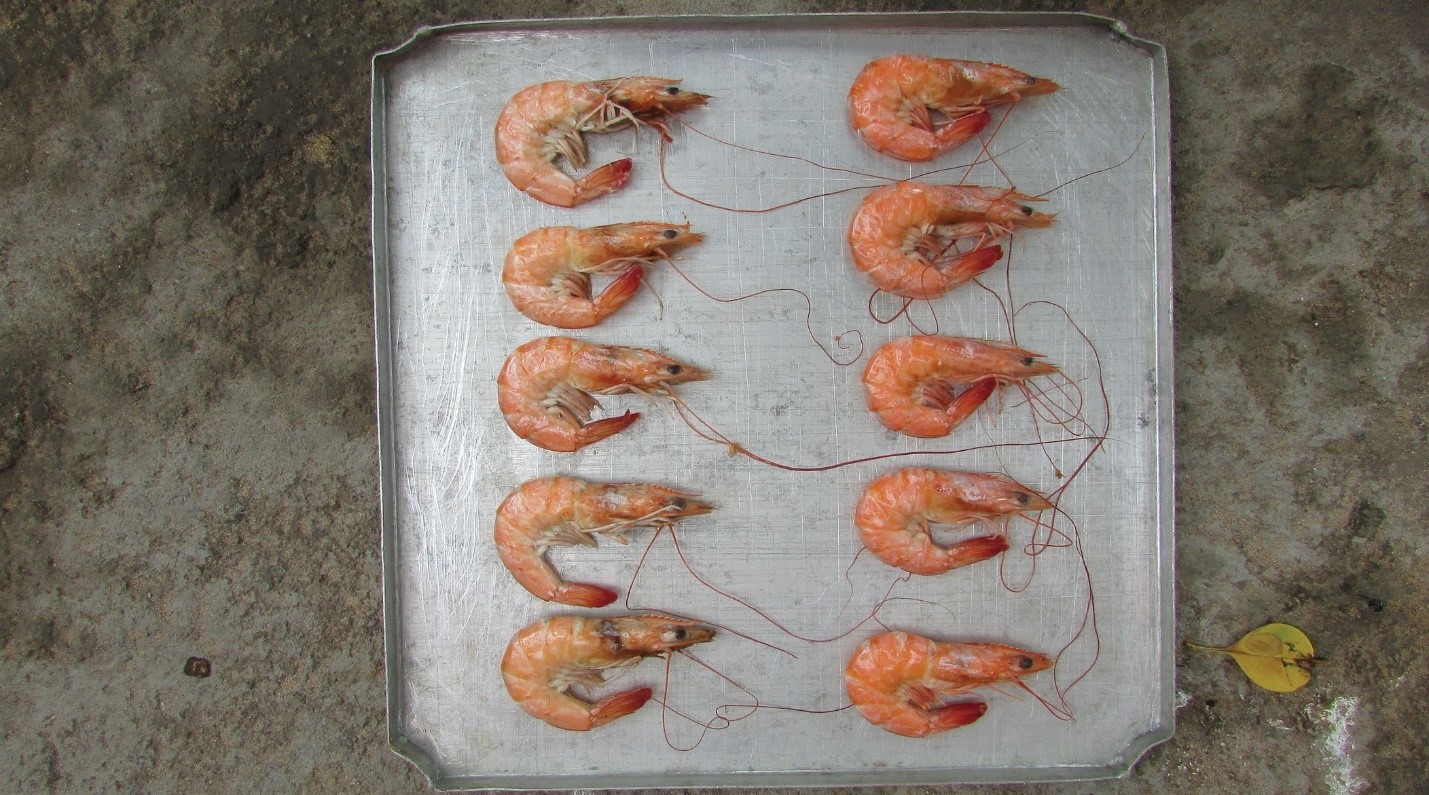

Shrimp with brown shell after being cooked (left), white shrimp after being cooked (right).
An important difference in the red (a*) value and a very small difference in the lightness (L*) and yellow (b*) values were observed between white and brown shrimp.
Analytical results: red color (a *) was significantly higher (P < 0.05) in blue-white shell shrimp, both fresh shell (7.9 ± 0.3) and cooked shell (17.9 ± 0). ,8), brown shell shrimp (4.8 ± 0.3 fresh samples, 14.4 ± 1.6 samples and cooked samples) showed differences between the two types of vannamei.
The main carotenoid pigment responsible for the color of shrimp is astaxanthin i.e. 3,3 dihydroxy β carotene 4,4-dione5,6. Before shrimp is cooked, astaxanthin is covered with protein chains called crustacyanins. Protein chains encapsulate astaxanthin and mask its reddish-pink color. The pigment content in shrimp shells is always higher than in abdominal muscles. Based on the results, it can be concluded that white-shelled white shrimp have more red cooked shrimp products than brown-shelled white shrimp.
Analysis of meat composition and texture
The protein, fat, calcium, potassium and sodium content, and cellular structure of the 2 types of shrimp were analyzed.
Results of analysis of meat composition: white shrimp has higher sodium content (552 mg%) and calcium (264mg%) than brown white shrimp (sodium 331mg%, calcium 188mg%) showing weight loss. Minerals can be a reason for the difference in shell color. The analysis results also showed that the white and blue shell shrimp had better meat texture.
Cause of shrimp color difference: probably due to stress brown shrimp. Some of the known factors that affect the color of farmed shrimp are when contaminated with a variety of bacteria or in a toxic culture environment. Martinez et al (2014) showed that the red color in shrimp could be the result of copper exposure. Metals such as cadmium, copper, lead and mercury combine with astaxanthin and form new complexes with a darker red color.
Conclusion:
The scientists also suggested that further studies are needed to identify the stress factors responsible for the differences in shell color of farmed shrimp.
Reported by: B. Madhusudana Rao, P. Viji and Jesmi Debbarma